
Have you ever wondered how photographers capture stunning images with a beautifully blurred background? The secret lies in a fascinating technology known as the “blur box”. This innovative algorithm utilizes the principles of physics, optics, and digital processing to create a visually pleasing and artistic effect.
Depth of field, often referred to as DOF, is a fundamental concept in photography. It determines the range of distance within an image that appears in sharp focus. When a photographer manually adjusts the focus of the camera, the lens and aperture work together to control the amount of light entering the sensor and consequently the amount of blur in the image.
The blur box technology takes this manual focus a step further by automatically creating a bokeh effect in the background. Bokeh refers to the aesthetic quality of the out-of-focus areas in an image. By selectively blurring certain pixels, the blur box algorithm mimics the natural way human vision perceives depth and creates a pleasing sense of depth and dimension in the photograph.
How does the blur box work? The algorithm analyzes the visual information captured by the camera’s sensor and identifies the elements in the foreground and background of the image. Using advanced image processing techniques, it applies a blur effect to the background pixels while keeping the subject sharp and in focus. This allows the viewer’s eyes to be drawn to the main subject, creating a captivating and professional-looking photograph.
The concept of the blur box
The blur box is a fascinating concept in the world of photography that involves the manipulation of a camera’s aperture, shutter speed, and lens to create a focused foreground and a blurred background. It is achieved through the physics and technology of optics and the perception of the human eye.
When we take a photograph, the camera works by capturing light through a lens and focusing it onto a digital sensor or film. The lens has the ability to adjust its aperture, which controls the amount of light entering the camera. This, in turn, affects the depth of field of the image – the range of distances that appear sharp and in focus.
The concept of the blur box revolves around manipulating the depth of field to create a visually appealing effect. By setting a wider aperture, a smaller portion of the scene is in sharp focus, while the rest of the image appears blurry. This blurring effect, known as bokeh, adds a sense of depth and separation between the foreground and background, allowing the subject to stand out.
The camera’s manual focus and automatic focus features also play a significant role in creating the desired blur effect. With manual focus, the photographer has full control over which part of the scene to sharpen, while automatic focus utilizes an algorithm to detect and focus on the intended subject. These features enable photographers to create beautifully blurred backgrounds while keeping the foreground sharp.
Additionally, digital image processing has a part to play in enhancing the blur effect. Algorithms in the camera’s software analyze the captured image and manipulate the pixels to increase the perception of depth and blur. This technology works hand in hand with the optics of the lens to produce the desired visuals.
The concept of the blur box is a perfect blend of science and art, showcasing the capabilities of photography and the human eye. Understanding the principles of physics, optics, and the technology behind cameras allows photographers to create captivating images that manipulate the viewer’s perception and evoke emotions through the clever use of blur and sharpness.
Understanding the principles

The blur box technology is based on the principles of perception, image processing, and sensor physics. To understand how it works, we need to delve into the physics of optics and the concepts of depth of field and bokeh in photography.
When capturing an image, a camera’s lens focuses light onto its sensor, creating a sharp representation of the scene. The lens aperture controls the amount of light entering the camera, affecting the depth of field, which determines the range of distances in focus. A smaller aperture results in a larger depth of field, while a larger aperture creates a narrower depth of field with a blurry background.
However, in the digital world, achieving a blurred background manually can be challenging, especially when using smartphones or compact cameras with fixed lenses. This is where the blur box technology comes into play. It uses an algorithm to simulate the bokeh effect by adding a blur effect to the background of an image.
The algorithm analyzes the pixels in the foreground and applies the appropriate level of blur to the background. By mimicking the way our visual perception operates, the blur box technology creates a realistic and aesthetically pleasing blur effect.
It’s important to note that the blur box technology works differently from a shallow depth of field achieved by using a wide aperture and a high-end lens. While the latter creates a natural and optical blur, the blur box technology enhances the background blur digitally.
In conclusion, the blur box technology utilizes a combination of optics, image processing algorithms, and sensor physics to create a visually appealing blur effect. By understanding these principles, we can appreciate the art and science behind this innovative technology.
Light and refraction

In the field of science, particularly in the field of optics and perception, light and refraction play a crucial role in how we perceive images. When light passes through a lens, it undergoes a process called refraction. This process causes the light rays to change direction as they pass through the lens, resulting in the formation of an image. The study of light and refraction is an integral part of physics and forms the foundation of many technologies, including photography and digital imaging.
When we take a photograph, the camera lens, aperture, shutter, and sensor all work together to capture the image. The camera lens focuses the incoming light onto the sensor, and the aperture controls the amount of light that enters the camera. The shutter determines the duration of exposure, allowing the sensor to capture the image correctly.
One of the factors that affect the sharpness of an image is the depth of field. This is the range of distances in front of and behind the subject that appears acceptably sharp in the image. The depth of field can be controlled by adjusting the aperture of the camera. A wide aperture (low f-number) results in a shallow depth of field, while a narrow aperture (high f-number) increases the depth of field, keeping more of the image in focus.
However, sometimes we want to achieve a blurred background in our photographs, also known as bokeh. The blur box algorithm can help us achieve this effect. By selectively blurring the background while keeping the foreground sharp, the blur box creates a visually pleasing image.
The blur box algorithm works by analyzing the image and identifying the areas that should be in focus and the areas that should be blurred. It does this by considering various factors such as depth of field, distance from the camera, and the amount of light hitting each pixel on the sensor.
The technology behind the blur box algorithm involves sophisticated image processing techniques. The algorithm analyzes the image pixel by pixel, determining the level of blur to apply to each pixel based on its position in the scene and the desired depth of field. By selectively blurring the background while keeping the foreground sharp, the blur box algorithm creates a visually appealing and aesthetically pleasing image.
In conclusion, the science behind the blur box and its ability to create a blurry background in photographs is rooted in the principles of light and refraction. By understanding the physics of how light behaves when passing through a lens, we can manipulate the light and create stunning images with a blurred background. The combination of technology and manual adjustments allows us to achieve the desired effect and capture images that are visually captivating.
Optical illusion
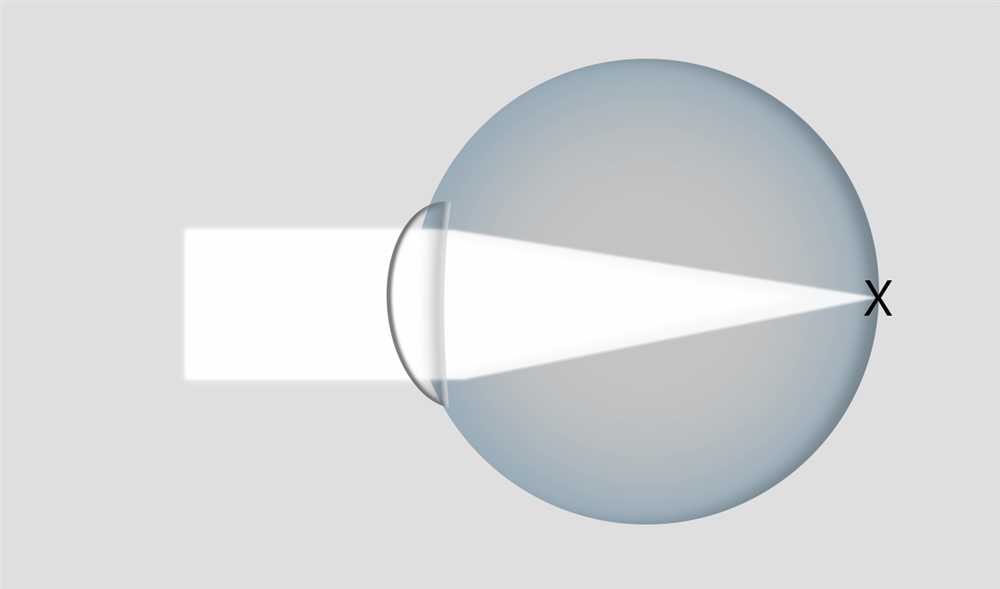
An optical illusion is a phenomenon where our visual perception differs from the actual physical properties of an object or image. It occurs due to the complex interaction between our eyes, brain, and the surrounding environment. Understanding optical illusions requires knowledge of fields like physics, optics, and psychology.
One common type of optical illusion is the blur effect, which creates the perception of a blurry image. This effect is often used in photography and digital image processing to enhance certain aspects or evoke specific emotions.
In photography, the blur effect is typically achieved by manipulating the camera’s focus, aperture, and shutter speed. By adjusting these settings, the lens captures light in a way that creates a shallow depth of field, where only a specific area is in sharp focus, while the foreground and background appear blurry. This technique is often used in portrait photography to draw attention to the subject and create a visually pleasing bokeh effect.
In digital image processing, the blur effect can be achieved through various algorithms. These algorithms work by manipulating the pixels in an image to simulate the optical blur effect. One common algorithm used for blurring is the Gaussian blur, which calculates the average color value of each pixel and its surrounding pixels to create a smooth, blurry transition.
The concept of blurring and creating optical illusions is also applicable to other areas, such as computer graphics and video games. In these fields, techniques like motion blur are used to simulate the effect of fast-moving objects or actions, creating a more realistic and immersive visual experience.
Overall, optical illusions, including the blur effect, are interesting phenomena that showcase the complexities of human perception and the remarkable advances in technology. Understanding the science behind optical illusions allows us to appreciate the intricacies of the visual world and the ways in which our eyes, brain, and environment work together to create our perception of reality.
The science of the blur box
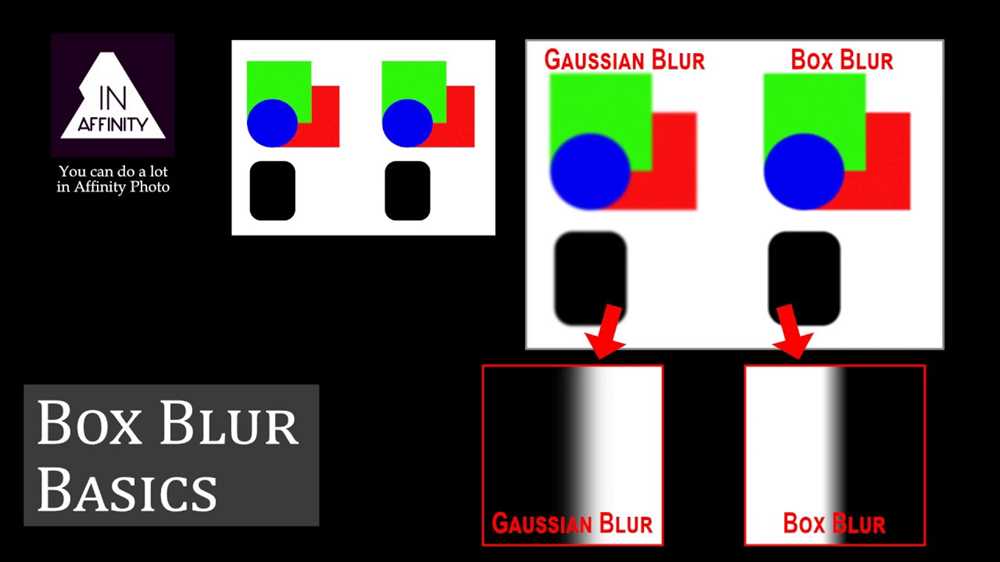
Photography is a visual art that relies on the processing of light. In order to capture a clear and sharp image, the camera’s technology must work in harmony with the laws of optics and physics. However, the science behind creating a blur in photography is just as fascinating.
Blur, often referred to as bokeh, is a term used to describe the out-of-focus areas in an image. It adds depth and dimension to a photograph, directing the viewer’s attention to the sharp foreground. The blur box, also known as the depth of field box, is an algorithmic feature that allows photographers to manually control the amount of blur in the background.
This algorithm takes advantage of the camera’s sensor, which is made up of millions of tiny pixels. When the shutter is released, each pixel captures a fraction of the light that enters the lens. However, not all pixels are created equal. In order to create a blurry background, the photographer adjusts the aperture, which determines the size of the opening through which light enters the camera. A wider aperture creates a shallower depth of field, resulting in a more pronounced blur.
The blur box algorithm then calculates the distance between the camera and the subject, as well as the distance between the subject and the background. By taking into account these distances, the algorithm determines which areas of the image should be in focus and which should be blurred. The result is a photograph with a sharp foreground and a beautifully blurred background.
Understanding the science behind the blur box can enhance one’s perception and appreciation for the art of photography. It highlights the intricate relationship between technology and creativity, demonstrating how a simple adjustment can transform a photograph into a work of art.
In conclusion, the blur box is a testament to the advancements in photography and the ever-evolving intersection between science and art. It is a powerful tool that allows photographers to control the visual perception of depth and create stunning images that capture the viewer’s attention.
Depth perception
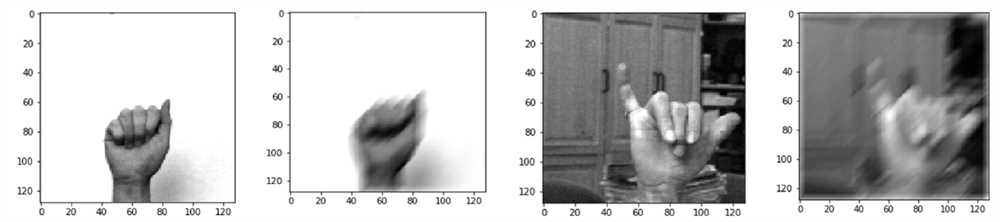
Depth perception is a crucial aspect of our visual perception that allows us to perceive and understand the three-dimensional world around us. It enables us to determine the distance and relative positions of objects in our environment.
Light plays a significant role in our depth perception. When light reflects off objects, it enters our eyes through the pupils and reaches the retina. The retina contains specialized cells called photoreceptors, which are responsible for converting light into electrical signals that our brains can interpret.
Digital cameras use various techniques to mimic the depth perception of the human eye. One such technique is controlling the depth of field, which is affected by the camera’s aperture and focus settings.
The aperture of a camera lens controls the amount of light entering the camera and influences the depth of field. A wide aperture (small f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, resulting in a blurry background and a sharp foreground. On the other hand, a narrow aperture (large f-number) produces a larger depth of field, resulting in a sharper image throughout the scene.
The focus settings of a camera determine the distance at which objects appear sharp. By adjusting the focus manually or using autofocus technology, photographers can achieve different levels of depth perception in their images.
The camera’s sensor and shutter also play a role in depth perception. The sensor captures the light that enters the camera and converts it into digital information. The shutter controls the exposure time, affecting how motion is captured in the image.
Depth perception is not limited to the hardware of the camera; it also involves post-processing algorithms that enhance the perception of depth in digital images. These algorithms analyze the distribution of colors, textures, and edges in an image to differentiate between the foreground and the background.
One of the visual effects commonly associated with depth perception is bokeh. Bokeh refers to the aesthetic quality of the out-of-focus areas in an image. It is created by intentionally blurring the background while keeping the foreground in sharp focus.
Depth perception is a fascinating field that combines principles of optics, physics, and psychology. Understanding how our eyes and cameras perceive depth can greatly enhance our ability to capture and appreciate the three-dimensional world through photography and other visual technologies.
How does the blur box work?
The blur box works by capturing the image with a camera and then applying a blur filter to the image using software algorithms.
What is the purpose of the blur box?
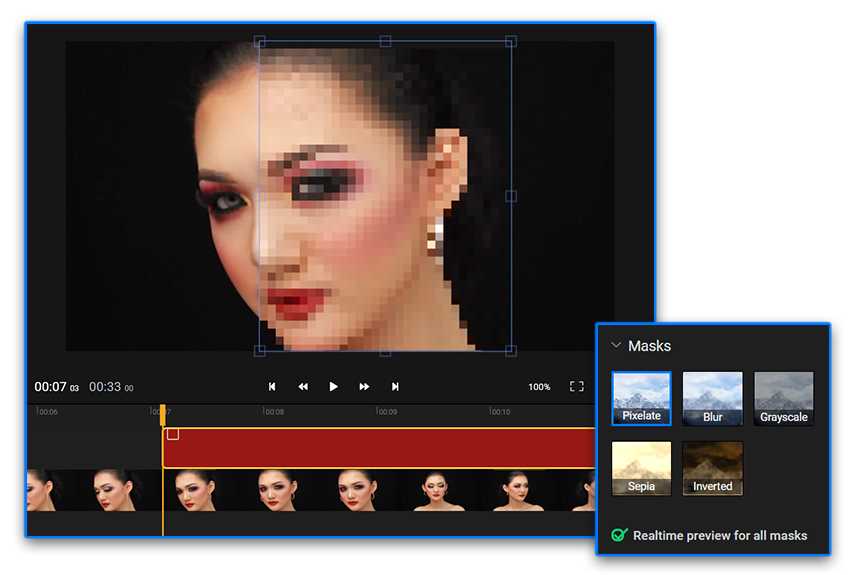
The purpose of the blur box is to obscure sensitive or private information in a photograph, such as license plates, faces, or other identifying details.
Is the blur box effective in hiding information?
Yes, the blur box is usually effective in hiding information. The blur filter applied to the image makes it difficult for people to read or recognize the obscured data.
Are there any limitations to the blur box?
Yes, there are some limitations to the blur box. In certain cases, the blur filter may not completely hide the information, especially if the image is of low quality or if the sensitive details are too small. Additionally, it may be possible for skilled individuals to reverse-engineer the blur and uncover the original information.
Can the blur box be applied to videos as well?
Yes, the blur box can be applied to videos as well. The same software algorithms used to apply the blur filter to images can also be used to process video frames and obscure sensitive information.








+ There are no comments
Add yours