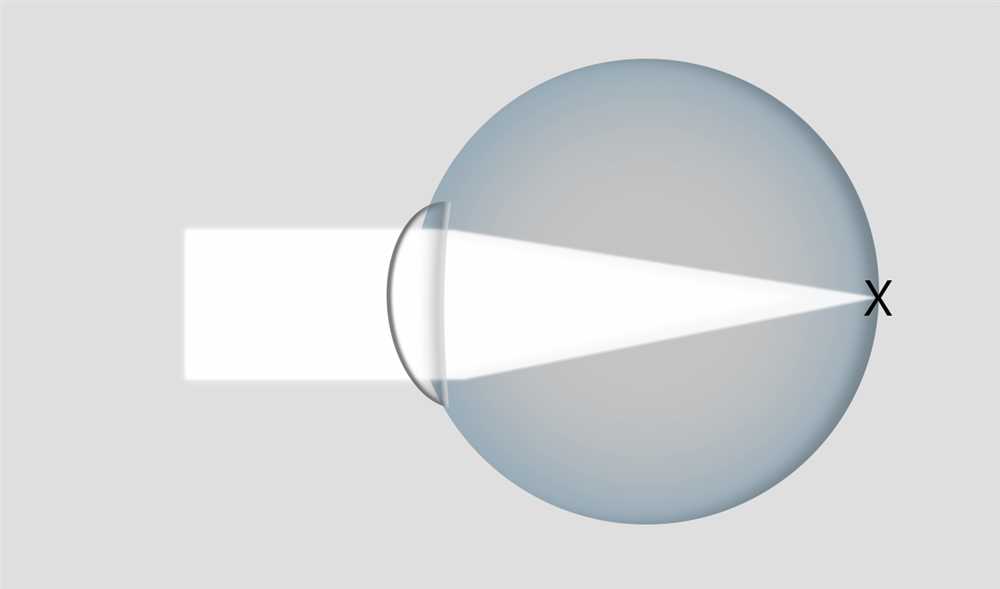
Blurry vision can have a profound influence on our perception of the world. Our eyes are the windows through which we interact with our surroundings, and when our vision is distorted, it can affect our subjective clarity and distortion of reality. The optical impairment of blurriness has long fascinated scientists and psychologists alike, leading to extensive study of its cognitive and psychological effects.
Researchers in the field of neuroscience have sought to examine the psychological impact of blurry vision through careful research and analysis. In one notable experiment, participants were asked to perform a series of tasks while wearing special glasses that distorted their visual perception. The results showed that the blur negatively affected their attention and ability to focus, leading to reduced cognitive performance.
Moreover, this blurry impairment extends beyond mere vision and appearance. It can also influence our emotional state and mood. Studies have shown that blurry perception can evoke feelings of anxiety and stress, as our brain struggles to make sense of the world around us. This psychological impact of blurriness highlights the intricate relationship between science and psychology, as researchers seek to unravel the complexities of our perceptual experience.
Exploring the Visual Impairment
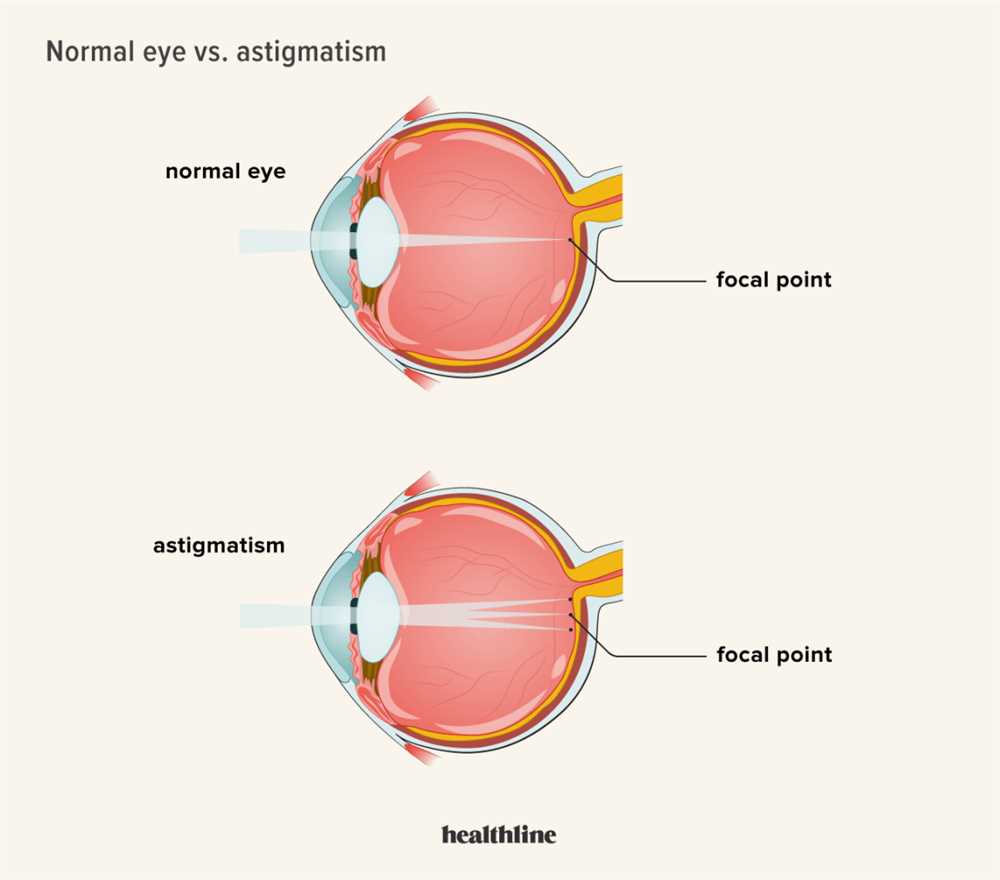
In the field of psychology, understanding the effects of visual impairment has been an ongoing area of research. Psychologists and researchers aim to examine the subjective experience of individuals with visual impairments and how it influences their cognitive processes and psychological well-being.
One aspect of visual impairment that has been widely studied is blurriness. Blurriness can be caused by various factors, such as optical distortion or a lack of clarity in one’s vision. To better understand the psychological effects of blurriness, scientists have conducted experiments to analyze its influence on attention, focus, and overall visual perception.
Through these experiments, researchers have found that blurry and distorted visuals can have a significant impact on the way individuals perceive their environment. The appearance of blurriness can lead to difficulties in identifying objects, recognizing faces, and processing visual information accurately. This cognitive challenge can affect a person’s daily functioning and social interactions.
Neuroscience studies have shown that the brain adapts to visual impairment by relying on other sensory information and cognitive processes. This adaptation helps individuals compensate for the lack of visual clarity, but it also highlights the plasticity of the brain and its ability to adjust to changes in sensory input.
Psychologists and researchers continue to explore the psychological effects of visual impairment to develop interventions and strategies that can improve the quality of life for individuals with blurry vision. By understanding the cognitive processes and subjective experience associated with visual impairments, scientists aim to develop methods that can enhance visual rehabilitation and provide support for those affected.
| Key Points |
|---|
| – Visual impairment can lead to blurriness and distortion in one’s vision. |
| – Blurriness can affect attention, focus, and overall visual perception. |
| – The brain adapts to visual impairment by relying on other sensory information and cognitive processes. |
| – Understanding the psychological effects of visual impairment can lead to improved interventions and strategies. |
Implications for Daily Tasks
The impairment of visual clarity and the presence of blurriness can have significant implications for various daily tasks, both practical and psychological. When our eyes perceive blurriness or distortions in our visual field, it can affect our appearance, cognitive functions, and overall well-being.
Subjective blur can influence our self-perception and self-confidence. When we experience blurriness in our vision, we may become self-conscious about our appearance. This can affect our social interactions and interactions in the workplace. Individuals with blurry vision may feel less confident and have difficulty maintaining eye contact, which can impact their professional and personal relationships.
From a cognitive perspective, blurriness can affect our attention and focus. The science of vision and research in neuroscience has shown that when our visual system is struggling to perceive clarity, it requires more cognitive resources to process visual information. This cognitive demand may lead to decreased performance on tasks that require visual analysis and interpretation, such as reading, driving, or operating machinery.
Psychological effects of blurriness also extend to our overall psychological well-being. Research and psychological studies have shown that individuals with blurry vision may experience higher levels of anxiety and stress. The constant effort to compensate for impaired vision can lead to mental fatigue and decreased quality of life.
Understanding the implications of blurriness in daily tasks is important for both individuals with blurry vision and professionals in fields such as psychology and optical science. By examining the influence of blurriness on various tasks, we can develop strategies and interventions to help individuals cope with and overcome these challenges. Additionally, further research and experimentation in the field of visual perception can lead to advancements in vision correction techniques and technologies.
The Cognitive Impact of Blurriness

The understanding of how blurriness affects cognitive processes is a fascinating area of study within the field of psychology. Researchers examine how impaired vision and blurred clarity can influence our visual perception and attention.
Science has shown that when our eyes experience blur or distortion, it can have both objective and subjective effects on our cognition. In optical experiments, participants with blurry vision often struggle to process visual information accurately, leading to difficulties in focus and concentration.
Psychologists and neuroscientists have conducted various studies to explore the impact of blurriness on cognitive functions. These studies have revealed that blurry vision can significantly impair cognitive tasks, such as reading, problem-solving, and memory recall. The distortion in visual input hinders our ability to process information efficiently and accurately.
Moreover, blurry vision can also affect our perception and interpretation of the world around us. The brain tries to compensate for the lack of clarity, but this compensatory process requires additional cognitive resources, which can lead to mental fatigue and decreased performance.
Research in cognitive psychology has also revealed that blurred vision can affect our attentional processes. When there is a lack of visual clarity, our attention tends to be drawn to the source of the blurriness, making it challenging to focus on other relevant information in our environment.
In summary, blurriness can have significant cognitive effects on individuals. The distortion and impairment in visual clarity can impact cognitive processes such as perception, attention, focus, and memory. Understanding these psychological effects is crucial for psychologists and researchers in developing interventions and strategies to improve visual clarity and mitigate the cognitive challenges associated with blurriness.
Evaluating the Attentional Resources

When it comes to understanding the psychological effects of blurriness, it is essential to examine the attentional resources that play a significant role in our visual focus. The field of neuroscience has conducted extensive research to shed light on the clarity impairment and distorted effects caused by blurriness. Scientists and psychologists have delved into the science of blur, both in terms of its optical and cognitive aspects.
One area of study is the subjective perception of blurry vision. By conducting experiments and analysis, psychologists aim to understand how attention influences our perception of blurriness. They examine how the appearance of objects changes when our attention is focused elsewhere or divided among multiple tasks.
In these experiments, participants are presented with stimuli that vary in clarity and are asked to rate their subjective experience of blurriness. Through careful analysis, researchers can distinguish between different levels of blurriness and the psychological impact it has on individuals.
Additionally, the influence of blurriness on cognitive processes has also been studied. Researchers have found that cognitive tasks requiring visual information processing can be impaired by the presence of blurriness. The cognitive workload increases as the clarity of vision decreases, resulting in decreased performance on tasks that rely heavily on visual processing.
Overall, understanding the attentional resources involved in perceiving blurriness is crucial for comprehending its psychological effects. The findings from these studies contribute to our knowledge of how our eyes and brain interpret visual stimuli, shedding light on the complex relationship between vision and cognition.
Memory and Retention Challenges
Psychology and cognitive science have long been interested in understanding how visual perception affects memory and retention. When we perceive the world around us, our subjective experience is influenced by various factors, including the clarity of our visual perception. When our vision is impaired or distorted due to optical blur, it can have significant effects on our psychological well-being.
Research has examined how the psychological effects of blurriness can influence our memory and retention abilities. In one study, participants were asked to examine a series of images with varying degrees of blur. After viewing the images, they were given a memory task to test their ability to remember specific details. The experiment found that participants had more difficulty recalling details accurately when the images were blurry compared to when they were clear.
In addition to affecting our ability to accurately remember visual information, blurriness can also impact our ability to focus attention. When our eyes struggle to perceive a clear image, it requires more cognitive effort to maintain focus and concentration. This increased effort can lead to cognitive fatigue and reduced performance in tasks that require sustained attention.
Furthermore, the appearance of blurriness can also influence our perception and interpretation of the world around us. Studies have shown that when visual stimuli are distorted or blurry, they can affect our overall understanding and interpretation of the scene. This can result in misperception or misinterpretation of visual information, leading to potential memory and retention challenges.
Understanding the psychological implications of blurriness and the challenges it poses to memory and retention is crucial for psychologists and neuroscientists alike. By studying the effects of optical blur on cognitive processes, researchers can gain insight into how our visual perception influences our ability to encode and retrieve information accurately. This understanding can help develop strategies to mitigate the negative effects of blurriness on memory and retention, ultimately improving our overall cognitive performance.
The Emotional Consequences
When our vision is impaired and our perception is distorted, it can have profound effects on our emotions and psychological well-being. A study conducted by neuroscientists and psychologists sought to examine the influence that blurry vision and visual distortion have on our emotional state.
In the experiment, participants were exposed to varying levels of optical blur and distortion, ranging from mild to severe. The researchers found that as the level of blur and distortion increased, participants reported feeling more anxious, frustrated, and even depressed. This suggests that the appearance of blurriness in our visual field can have a significant impact on our psychological state.
Interestingly, the subjective experience of blurriness also influenced participants’ attention and focus. When their vision was blurry, participants found it more difficult to concentrate on tasks and were easily distracted. This impaired ability to maintain clarity of vision was found to be associated with feelings of frustration and decreased confidence.
Further analysis of the data revealed that the psychological effects of blurriness were not solely related to the impairment of physical vision. Rather, the distortion of visual perception seemed to tap into broader psychological processes. The blurred and distorted appearance of the environment created a sense of uncertainty and instability, leading to heightened feelings of anxiety and unease.
This research highlights the complex relationship between our visual perception and our emotional well-being. It underscores the importance of understanding the psychological effects of blurriness and the role it plays in shaping our overall mental state. By delving into the science behind blurriness, psychologists and researchers hope to gain further insights into how we can better support individuals who struggle with visual impairments and develop strategies to enhance visual clarity for improved psychological health.
Impact on Self-Perception

Blurriness can have a significant impact on our self-perception. Research has shown that the way we perceive ourselves is strongly influenced by our visual appearance, and when that appearance is compromised by optical impairments such as blurriness, it can have psychological effects.
Psychologists and cognitive scientists have conducted experiments to examine the subjective experience of blurriness and its effects on self-perception. One study used visual distortion goggles to simulate blurry vision and found that participants reported feeling more self-conscious and less confident in their appearance.
Neuroscience research has also shed light on the connection between blurry vision and self-perception. A study using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) showed that when participants viewed images of themselves with blurred features, areas of the brain associated with self-recognition and self-esteem showed decreased activation.
This analysis suggests that blurry vision can distort our perception of ourselves, leading to negative effects on self-confidence and self-image. The lack of clarity in our visual field may prevent us from accurately perceiving our own appearance and can influence how we think others perceive us.
The influence of blurriness on self-perception is not limited to our physical appearance. Blurry vision can also affect our cognitive abilities and attention. When our vision is impaired, we may struggle to focus on tasks and information in our environment, leading to feelings of frustration and decreased self-efficacy.
Understanding the science behind how blurriness impacts our self-perception is important for both individuals dealing with visual impairment and psychologists studying the effects of vision on mental well-being. By recognizing the psychological consequences of blurriness, we can develop interventions and strategies to support individuals in managing their perception and improving their overall confidence and self-esteem.
Social Interactions and Isolation
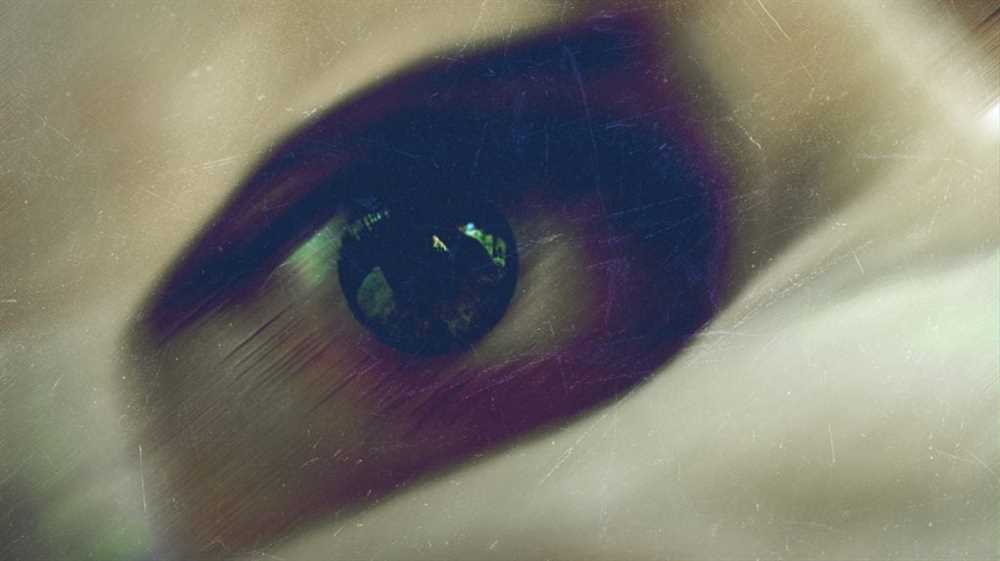

Visual appearance plays a crucial role in our social interactions. When we interact with others, our eyes serve as the primary means of communication, allowing us to perceive each other’s emotions and reactions. However, when our vision becomes blurry or distorted, it can have significant effects on our social interactions and feelings of isolation.
In a groundbreaking experiment conducted by scientists in the field of psychology and neuroscience, the effects of visual impairment on social interactions were examined. Participants were asked to wear special glasses that simulated different levels of blurriness and distortion in their vision. Through this experiment, scientists aimed to understand how the subjective experience of seeing blurry influences social interactions.
The results of the study revealed that blurriness and distortion in vision can have a profound impact on social interactions. Participants reported feeling self-conscious and anxious about their appearance when their vision was impaired. They were less confident in their ability to interpret social cues accurately and felt isolated from others. This suggests that blurry vision can lead to a decreased sense of social connection and contribute to feelings of loneliness and isolation.
From a cognitive perspective, blurriness and distortion in vision also affect our attention and perception. When our eyes struggle to focus and perceive clarity, our attention becomes divided, leading to difficulties in processing social cues and grasping the nuances of social interactions. This impairment in cognitive perception can lead to miscommunication and misunderstandings, further exacerbating the feeling of social isolation.
Understanding the psychological effects of blurriness on social interactions is crucial not only for individuals with visual impairments but also for the general population. Research in this field is advancing our understanding of the intricate relationship between vision and social interactions, and it has the potential to inform interventions and strategies that promote social inclusivity and well-being.
In conclusion, the science behind blurriness and its effects on social interactions is a fascinating area of research. By examining the subjective experience of blurry vision and its influence on social interactions, psychologists and neuroscientists are gaining valuable insights into the complexities of human perception and social behavior. This research highlights the importance of visual clarity not only for our physical well-being but also for fostering social connection and reducing feelings of isolation.
What is the scientific explanation for blurriness?
Blurriness occurs when the eye is unable to focus properly on an object. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including refractive errors, eye muscle problems, and certain eye conditions.
What are the psychological effects of blurriness?
Blurriness can have several psychological effects on individuals. It can cause frustration, stress, and a decreased quality of life. It can also lead to decreased self-confidence and affect social interactions.
How does blurriness affect daily activities?
Blurriness can greatly affect daily activities as it can make tasks such as reading, driving, and even recognizing faces difficult. It can slow down productivity and hinder overall performance in various tasks.
Can blurriness be treated?
Yes, blurriness can often be treated depending on the cause. Glasses, contact lenses, or corrective surgeries are commonly used to correct refractive errors. Eye exercises and therapy may also be recommended for certain eye muscle problems.
What steps can be taken to prevent blurriness?
To prevent blurriness, it is important to maintain good eye health. This includes regular eye examinations, practicing good eye hygiene, protecting the eyes from harmful UV rays, and avoiding excessive screen time. It is also important to address any existing eye conditions promptly.







+ There are no comments
Add yours