Perception is an intricate process that allows us to perceive and understand the world around us. Our visual system plays a crucial role in this cognitive and perceptual function, enabling us to interpret the movement of objects that cross our field of view.
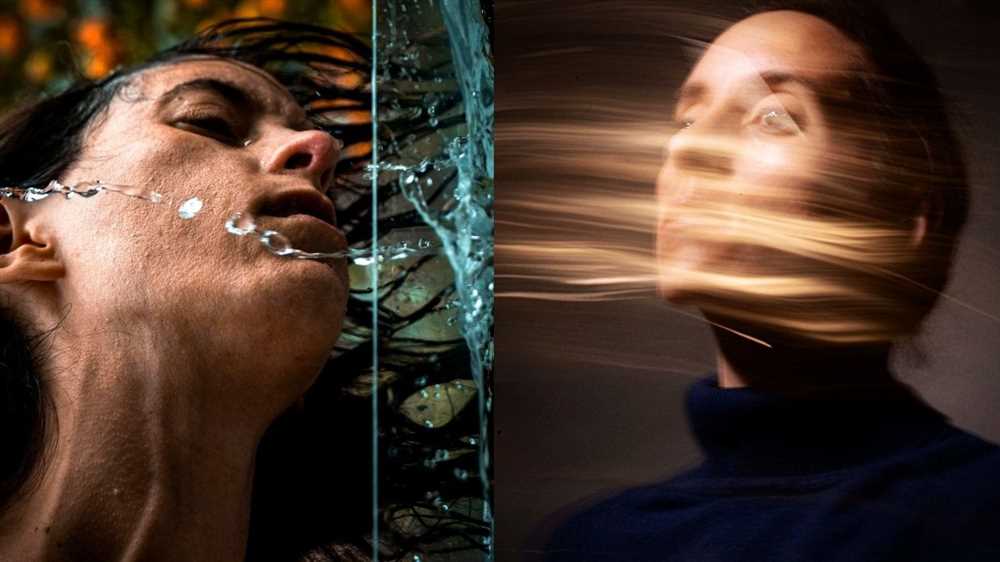
It is intriguing how our brain processes the visual input it receives from our eyes, especially when it comes to the perception of motion. The phenomenon of blur presents an interesting optical illusion that can have a profound effect on our subjective experience of speed and movement.
Blur occurs when the stimulus we perceive is not sharp or well-defined. As a result, our brain becomes more attentive to this ambiguity and disintegration of visual information. This illusory effect can create the sensation of motion even when there is no actual movement present.
Neuroscience has delved into the study of how our brains perceive motion and the impact that blurred stimuli have on our awareness and attention. It has been discovered that our perceptual system is finely tuned to detect motion cues, even in the absence of clear visual information. The brain utilizes various cues, such as changes in size, position, and texture, to infer movement.
In this article, we will explore the psychology behind the perception of blur and how this illusory phenomenon impacts our understanding of motion. We will delve into the subjective nature of blur and its perceptual consequences, shedding light on the intricate workings of our visual system.
The Impact of Motion Blur on Human Perception
Motion blur is a cognitive phenomenon that impacts the way we perceive visual stimuli in motion. The disintegration of sharp details into a blur creates an illusion of movement, which can affect our perception and understanding of the objects and scenes around us.
When our eyes track a moving object or scene, the stimulus generates a visual perception of motion due to motion blur. This perceptual effect is a result of the brain’s processing of the ambiguous and rapidly changing visual information. The speed of the movement and the level of blur influence the subjective sensation of movement and can impact our ability to accurately perceive and interpret the visual scene.
Motion blur is an optical effect that occurs when visual stimuli move faster than our visual system can process. This creates a temporal ambiguity, where the brain must integrate and interpret the changing information to create a coherent perception of movement. The level of blur can vary depending on factors such as the speed of the stimulus, the distance from the observer, and the duration of the exposure.
The impact of motion blur on perception is studied extensively in the fields of psychology and neuroscience. Researchers have found that motion blur can alter our attentional focus, making it more difficult to attend to specific details or objects within a scene. This can lead to a decrease in our ability to accurately perceive and remember visual information.
Furthermore, motion blur can affect our spatial perception, leading to errors in estimating the position, size, and depth of objects in a moving scene. The blurred edges and lack of sharp details can create an illusion of objects being closer or farther away than they actually are, resulting in misjudgments of distance and size.
Despite these perceptual challenges, motion blur can also have a positive impact on our visual experience. It can enhance the sense of speed and dynamic movement, creating a sense of excitement and energy in visual media such as movies and video games. The intentional use of motion blur in these mediums can provide a heightened sensation and immersive experience.
In conclusion, motion blur is a perceptual phenomenon that impacts our understanding and experience of movement. Its effects on attention, perception, and spatial awareness highlight the complex interplay between the visual system and the external world. Further research in the field of motion blur could deepen our understanding of the mechanisms behind this phenomenon and its implications for various aspects of human perception.
Cognitive Effects of Motion Blur
Motion blur, a phenomenon that occurs when there is a disintegration of visual stimuli due to motion, has a significant impact on perceptual processing and cognitive awareness. The subjective perception of motion blur can vary depending on several factors, including the speed of motion and the extent of optical blur.
Research in the field of neuroscience and psychology has shed light on how motion blur impacts our perception and understanding of the visual world. Our brain processes visual information received by our eyes in order to create a coherent and meaningful perception of movement. However, the illusion of motion blur can introduce ambiguity into this process, leading to perceptual and cognitive challenges.
When a stimulus is presented with motion blur, it can create an illusory sense of movement. This illusory motion can be particularly compelling when the blur is perceived to be moving across the visual field. The brain attempts to make sense of this ambiguous input by integrating visual cues such as direction and speed, which can result in a distorted perception of the actual motion.
The impact of motion blur on attention and sensation is an important area of study within cognitive psychology. This research has found that motion blur can influence the allocation of attention and the perception of visual motion. For example, studies have shown that motion blur can decrease perceptual acuity and impair the ability to accurately perceive object motion.
Furthermore, the cognitive effects of motion blur can extend beyond the moment of perception. Studies have suggested that motion blur can affect subsequent cognitive processing and decision-making. For instance, when presented with a moving object with motion blur, individuals may experience increased difficulty in accurately judging its trajectory or speed.
In conclusion, the illusion of motion blur has significant implications for our perception and understanding of the visual world. The cognitive effects of motion blur highlight the complexity of visual processing and the role of ambiguity in shaping our perception. By further investigating this phenomenon, we can deepen our understanding of the interaction between perceptual and cognitive mechanisms, ultimately enhancing our knowledge of the human brain and its capabilities.
Influence on Attention and Focus
The perceptual phenomenon known as the illusion of motion has long fascinated researchers in the field of neuroscience and psychology. Through the study of the visual system and the workings of the human brain, scientists have gained a deeper understanding of how this illusory movement impacts our perception and cognition.
One area where the illusion of motion has a significant influence is in our attention and focus. When presented with a stimulus that creates the perception of motion, our visual system automatically directs our eyes to track and follow the movement. This involuntary eye movement is a result of the brain’s attempt to maintain a clear and stable image of the moving object.
As our eyes track the illusory movement, our attention becomes fixated on the perceived motion. This attentional focus can have both positive and negative effects on our perceptual awareness. On one hand, the illusion of motion can enhance our awareness of visual stimuli, allowing us to better detect and process information that is presented in a dynamic and rapidly changing environment.
However, the illusory movement can also lead to a disintegration of our perceptual clarity. The ambiguity of the motion can result in a decrease in our ability to accurately perceive and understand the visual scene. This disintegration effect occurs because our brain is constantly trying to reconcile the conflicting information provided by the illusion of motion, leading to a decrease in the overall quality of our perception.
Furthermore, the cognitive processing speed required to perceive the illusion of motion can have an impact on our attentional capacity. The brain must allocate a significant amount of resources to process the illusory movement, which can reduce our ability to attend to other stimuli in the environment. This can lead to a narrowing of our attentional focus and a decrease in our overall awareness of our surroundings.
In conclusion, the illusion of motion has a profound influence on our attention and focus. It can enhance our perceptual awareness of visual stimuli, but it can also lead to a disintegration of our perception and a narrowing of our attentional focus. Understanding the optical and cognitive processes underlying this phenomenon is crucial for gaining insights into the subjective experience of motion and its impacts on our perception.
Effects on Memory and Recall
As humans, our optical perception is deeply intertwined with our psychology and awareness. The way we process visual information, especially motion, can significantly impact our memory and recall abilities. This phenomenon has been extensively studied in the fields of psychology, neuroscience, and perception, shedding light on the illusory nature of our perception and the subjective nature of our memory.
When we perceive motion, our brain combines information from our eyes and other cognitive processes to create a coherent representation of the world. However, when faced with blur or ambiguity in the visual stimulus, our brain struggles to process the information accurately. The illusory sensation of movement or motion blur can lead to distortions in our perception, affecting our ability to remember and recall specific details.
One of the key factors that impacts memory and recall is the speed at which the blur or motion occurs. Research has shown that slower speeds of motion can enhance our ability to remember visual information. This is because slower speeds allow more time for our brain to process the stimulus and form a stable memory. On the other hand, rapid or disintegrated motion can disrupt our cognitive processes, making it more challenging to retain and recall information accurately.
Furthermore, the attentional aspects of blur and motion play a critical role in memory and recall. Our attention is naturally drawn to movement, making it easier to perceive and remember moving objects compared to static ones. However, the blur can also distract our attention, decreasing our ability to focus on specific details and impairing memory formation and retrieval.
Additionally, the illusion of motion and blur can create perceptual ambiguities, making it difficult to differentiate between different objects or events. These ambiguities can lead to memory errors and false recollections, as our brain tries to make sense of the blurred information. Our brain might fill in the gaps in our memory with plausible but inaccurate details, leading to a distorted recollection of events.
In conclusion, the impact of the illusion of motion and blur on memory and recall is a complex and fascinating subject in the field of psychology. Our subjective perception, attentional processes, and cognitive abilities all contribute to how we perceive and remember blurred or moving stimuli. Understanding these effects can provide insights into how our brains process visual information and how motion perception impacts our everyday experiences.
Emotional Response to Motion Blur
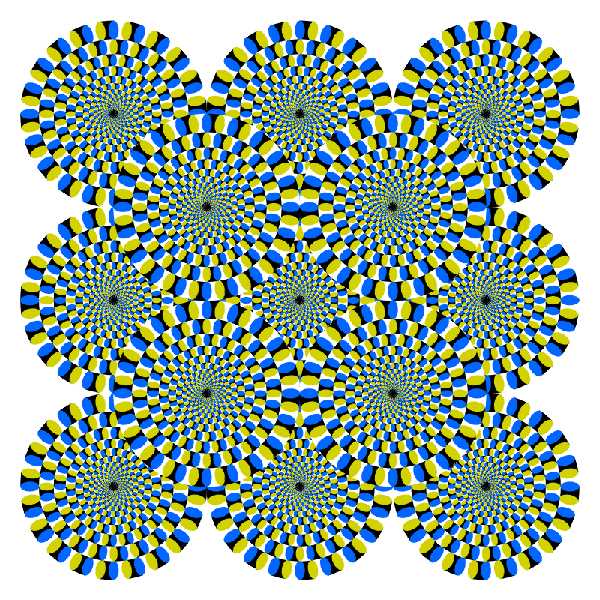
Motion blur is a cognitive phenomenon that impacts our perception of visual stimuli. It occurs when there is a lack of clarity or sharpness in the image due to the movement of objects. This illusion of motion can have a significant effect on our emotional response to what we perceive.
When we see motion blur, our brain registers it as a sign of movement and speed. This can evoke different emotional reactions depending on the context and the individual. For example, if we perceive a blurred image of a car racing towards us, we may experience fear or anxiety as a result of the perceived threat. On the other hand, if we see a blurred image of a loved one running towards us, we may experience excitement or happiness.
Our emotional response to motion blur is closely tied to our perceptual awareness and understanding of the world around us. The brain processes visual information and makes sense of it based on past experiences and expectations. When presented with a blurred stimulus, our brain tries to fill in the gaps and make sense of the movement.
Neuroscience research has shown that motion blur can lead to a heightened state of attention and processing in the brain. This is due to the perceived ambiguity and uncertainty of the visual information. Our brain becomes more engaged in trying to resolve the illusory motion, which can increase our emotional response.
It is important to note that the emotional response to motion blur is subjective and can vary from person to person. Some individuals may be more sensitive to the optical effect and experience stronger emotional reactions, while others may perceive it as a natural part of visual perception.
In conclusion, motion blur has a profound impact on our emotional response to visual stimuli. It influences our perception of movement and can evoke various emotions depending on the context. The subjective nature of this phenomenon highlights the complex relationship between psychology and visual perception.
Association with Excitement and Thrill

The psychology of blur is closely linked to the perception of speed and the experience of excitement and thrill. When we see a blurred object or motion, our awareness is heightened, and our eyes become more attentive to the stimulus. This subjective experience is often associated with a sense of high-speed movement, creating a sensation of excitement and thrill.
The optical illusion of motion blur tricks our perceptual system into perceiving movement where there might not be any. This phenomenon is a result of the brain’s processing of visual information, which tries to make sense of the ambiguity presented by the blur. Our cognitive system tries to fill in the missing details, resulting in a perceived sense of rapid movement.
The neuroscience behind this perceptual illusion suggests that attention plays a crucial role in how we perceive blur. When our attention is focused on a moving object, we are more likely to perceptually integrate the blurred information and perceive it as continuous motion. Our brain filters out irrelevant details and focuses on the essential aspects of the visual input.
The association between blur and excitement can be seen in various contexts. For example, in sports photography, capturing a fast-moving athlete with a blurred background can convey a sense of speed and dynamism. Similarly, in cinematography, using motion blur techniques can create a thrilling and immersive experience for the audience.
Understanding the psychological and perceptual impacts of blur is crucial in many fields, including design, advertising, and virtual reality. By harnessing the illusory effect of blur, designers can create visually appealing and engaging experiences that evoke excitement and thrill.
In conclusion, the association between blur, excitement, and thrill is a perceptual phenomenon linked to our cognitive processing. The subjective experience of speed and the optical illusion of motion blur can create a heightened sense of excitement and thrill. The psychology of blur provides valuable insights into how our brain processes visual information and impacts our perception.
What is the article about?
The article is about the psychology behind the illusion of motion and how it affects perception.
How does the illusion of motion impact perception?
The illusion of motion can have a significant impact on perception as it can alter our understanding of the visual world. It can influence how we perceive the speed and direction of objects, the size and shape of objects, and even our sense of time.
Can you give an example of how the illusion of motion affects perception?
Sure! For example, when watching a moving car from a distance, the illusion of motion can make the car appear closer than it actually is. This can lead to misjudgments of distance and affect our ability to accurately perceive the car’s speed.
What are some factors that contribute to the illusion of motion?
There are several factors that contribute to the illusion of motion, such as the presence of dynamic cues in the environment, the relative motion of objects, and the brain’s interpretation of visual input. Additionally, certain optical illusions, such as the motion aftereffect, can also create the illusion of motion.








+ There are no comments
Add yours