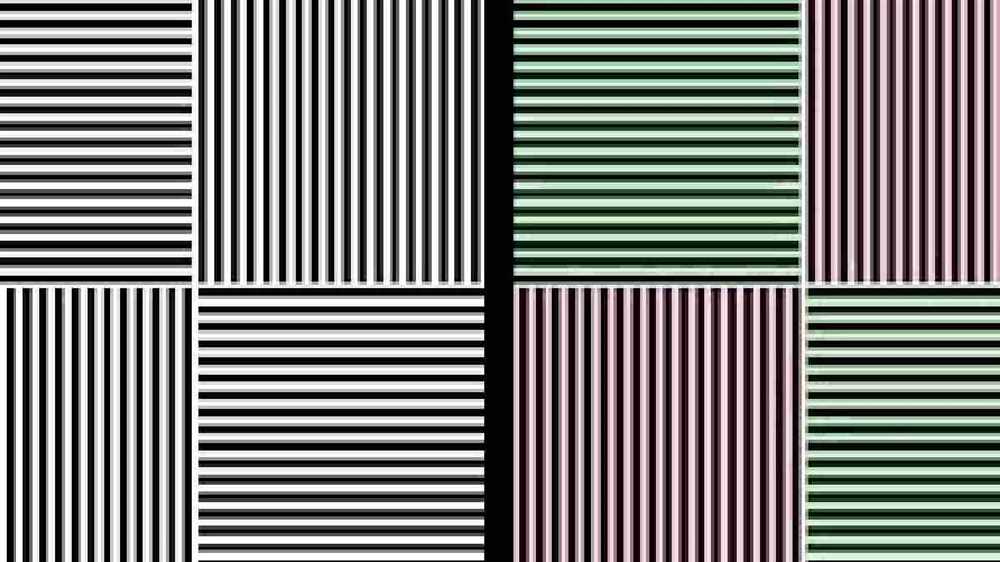
Optical illusions have long fascinated the human mind, captivating our imagination and challenging our interpretation of reality. These enigmatic phenomena, often referred to as visual illusions, blur the line between perception and deception, enticing us to question the limitations of our cognitive awareness. From the depths of neuroscientific research to the intricacies of our own individual experiences, optical illusions provide a unique window into the inner workings of the human brain.
In the realm of psychology, the study of optical illusions has shed light on the intricate process of visual perception. Our brains are constantly bombarded with an array of stimuli, and the ability to perceive and interpret this sensory information plays a crucial role in our understanding of the world. However, optical illusions challenge our perspective by distorting the visual stimuli that our brain receives, revealing the complex interplay between our perceptions and the external reality.
By exploring the psychological effects of optical illusions, scientists have unraveled the profound impact these phenomena have on our perception and cognition. These illusions have the power to deceive our brain and alter our vision, leading researchers to question the very nature of reality. Through studying the neural mechanisms that underlie these perceptual distortions, scientists have discovered that illusions can reveal fundamental insights into the workings of our brain and the intricacies of our visual system.
The effects of optical illusions extend far beyond mere entertainment or curiosity. Understanding how our brain perceives and processes visual illusions can shed light on a range of psychological and neurological conditions. By deciphering the neural pathways and mechanisms involved in optical illusions, researchers hope to gain deeper insights into conditions such as amblyopia, a disorder that affects the brain’s ability to process depth and perceive visual stimuli accurately.
The Science of Perception
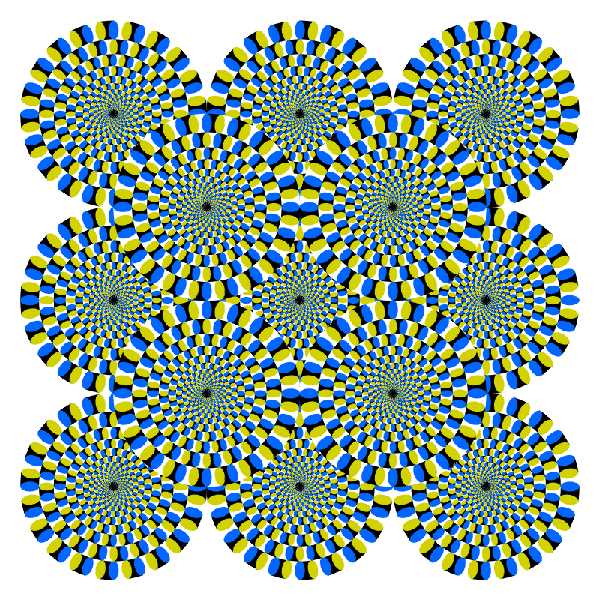
Perception is a complex cognitive process that involves the interpretation of sensory stimuli by the brain. It goes beyond the blur of optical illusions, allowing us to make sense of the world around us.
Understanding perception is a field of study that combines neuroscience and psychology to investigate how the mind processes and interprets visual information. Researchers use a variety of techniques to explore the effects of optical illusions on our perception, shedding light on the mechanisms behind this intriguing phenomenon.
Perceptual illusions occur when our brains perceive something different from what our senses detect. They reveal the limitations and biases of our visual system, challenging our understanding of reality. These illusions often exploit our brain’s reliance on heuristics and cognitive shortcuts, leading to distortions in our interpretation of the visual world.
Neuroscience research has shown that our perception is not simply a passive reflection of reality but an active process shaped by our attention, expectations, and prior experiences. The brain processes visual stimuli in parallel, using different regions to analyze different aspects of the visual scene, such as color, motion, depth, and shape.
Optical illusions can provide valuable insights into the workings of perception, as they allow us to investigate how our brains interpret visual information. By studying illusions, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of how our depth perception, object recognition, and spatial awareness function.
Beyond their scientific value, optical illusions also intrigue us and challenge our perception. They remind us that what we see may not always be an accurate representation of reality, highlighting the subjective nature of our visual experience.
In conclusion, the science of perception delves into the fascinating realm of cognitive psychology and neuroscience, exploring the intricacies of how we perceive the world around us. By studying optical illusions and their effects on our perception, researchers aim to unravel the mysteries of the mind and uncover the underlying mechanisms that shape our visual experience.
The Brain’s Role in Optical Illusions

Optical illusions have long fascinated scientists and researchers in the field of neuroscience. These illusions challenge our perception of reality and offer valuable insights into how the brain processes visual information.
Illusions are visual distortions that go beyond the interpretation of simple visual stimuli. They occur when our brain misinterprets or misinterprets the incoming information, leading us to perceive something different from what is actually there. Optical illusions can range from simple illusions, such as the famous Müller-Lyer illusion, to more complex illusions, such as the Ames room illusion.
Research in neuroscience has shown that optical illusions are not only a result of visual stimuli but also involve cognitive processes in the brain. This interdisciplinary field combines knowledge from psychology, neuroscience, and cognitive science to better understand how the brain perceives and interprets the world around us.
When we perceive an optical illusion, our brain is actively trying to make sense of the visual information it receives. It relies on a network of neurons and connections that work together to process and interpret the incoming signals. The brain’s attention, awareness, and depth perception all play a role in how we perceive optical illusions.
One theory suggests that optical illusions occur because our brain relies on heuristics and shortcuts to interpret visual information. These shortcuts can sometimes lead to errors in perception, resulting in illusions. For example, in the Müller-Lyer illusion, our brain misjudges the length of lines due to the arrowheads at the ends.
Understanding the mechanisms behind optical illusions can provide valuable insights into the workings of the mind and the effects of visual stimuli on our perception. It helps researchers and scientists gain a deeper understanding of how the brain processes information and how our perception can be influenced by external factors.
Overall, the study of optical illusions goes beyond a mere fascination with visual tricks. It is a scientific endeavor that aims to uncover the mysteries of the brain and the complexities of human perception. By studying illusions, researchers hope to gain a better understanding of the nature of the mind and how our brain constructs our perceptual reality.
Visual Processing and Interpretation

Visual perception is a complex process that involves the mind’s interpretation of visual stimuli. The effects of optical illusions on our visual awareness have long fascinated scientists and researchers in the field of psychology.
Optical illusions are visual phenomena that can distort our perception of objects, depth, and perspective. They deceive our brains by presenting conflicting or ambiguous information, tricking us into perceiving something that is not actually there.
The study of optical illusions goes beyond mere perception and delves into the realm of cognitive science and neuroscience. Research in these fields seeks to understand how the brain interprets visual information and how it can be tricked by optical illusions.
These illusions provide valuable insights into the workings of the brain and the limitations of our visual perception. They challenge our preconceived notions and showcase the complexity of the human mind’s ability to perceive and interpret the world around us.
Visual distortions caused by optical illusions can be attributed to the cognitive processes involved in visual perception. Our brains use previous knowledge and experience to make sense of incoming visual information, but this can sometimes lead to errors or misinterpretations.
Understanding the psychological effects of optical illusions requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining the fields of psychology, neuroscience, and cognitive science. This research helps unravel the intricacies of the human mind and sheds light on the mechanisms behind visual processing and interpretation.
In conclusion, optical illusions go beyond the blur of surface-level perception and provide a deeper understanding of the cognitive and psychological processes involved in visual interpretation. Exploring these phenomena through scientific research enhances our awareness of the complexities of visual perception and challenges our understanding of how we perceive the world.
The Role of Context in Perception
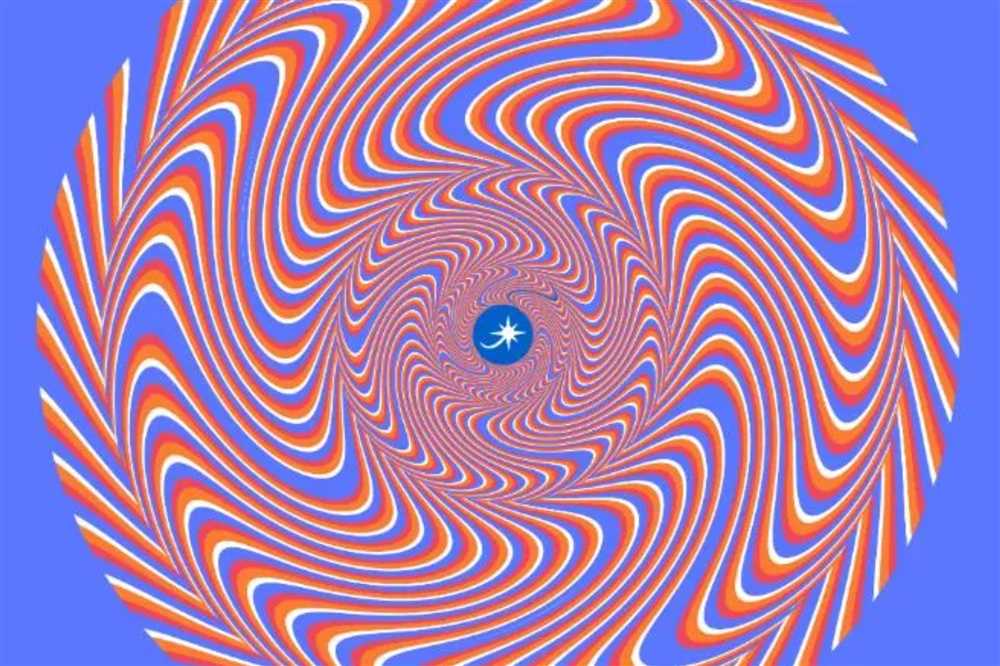

In the psychological and visual sciences, optical illusions have long fascinated researchers and captured the attention of the general public. These perceptual phenomena are characterized by the distortion of our visual awareness, leading us to perceive things that may not actually be there. The brain plays a crucial role in this intricate process, as it receives and interprets the information provided by our eyes.
One particular aspect that influences our perception of optical illusions is the role of context. The mind does not perceive visual stimuli in isolation; instead, it takes into account surrounding elements and the overall context to make sense of the visual information received. This cognitive process allows us to perceive depth, perspective, and differentiate between foreground and background objects.
Research in the field of neuroscience has revealed that the brain’s neurons are highly sensitive to contextual cues. These cues help the brain to determine the true nature of the stimuli and prevent us from falling into the deception of optical illusions. By analyzing the context, the brain can signal that what we perceive as a distortion is actually a result of the way our visual system processes information.
Beyond the world of optical illusions, the role of context in perception is evident in our everyday experiences. For example, when we enter a crowded room, our brain relies on contextual clues to help us identify familiar faces or objects amidst the chaos. Contextual information also aids us in understanding spoken language and interpreting social situations.
Understanding the role of context in perception is crucial for advancing our knowledge of the human mind and cognitive processes. By unraveling how our brain perceives the world around us, we can gain deeper insights into the mechanisms that guide our visual perception and contribute to our overall understanding of the complexities of human perception.
The Psychological Impact
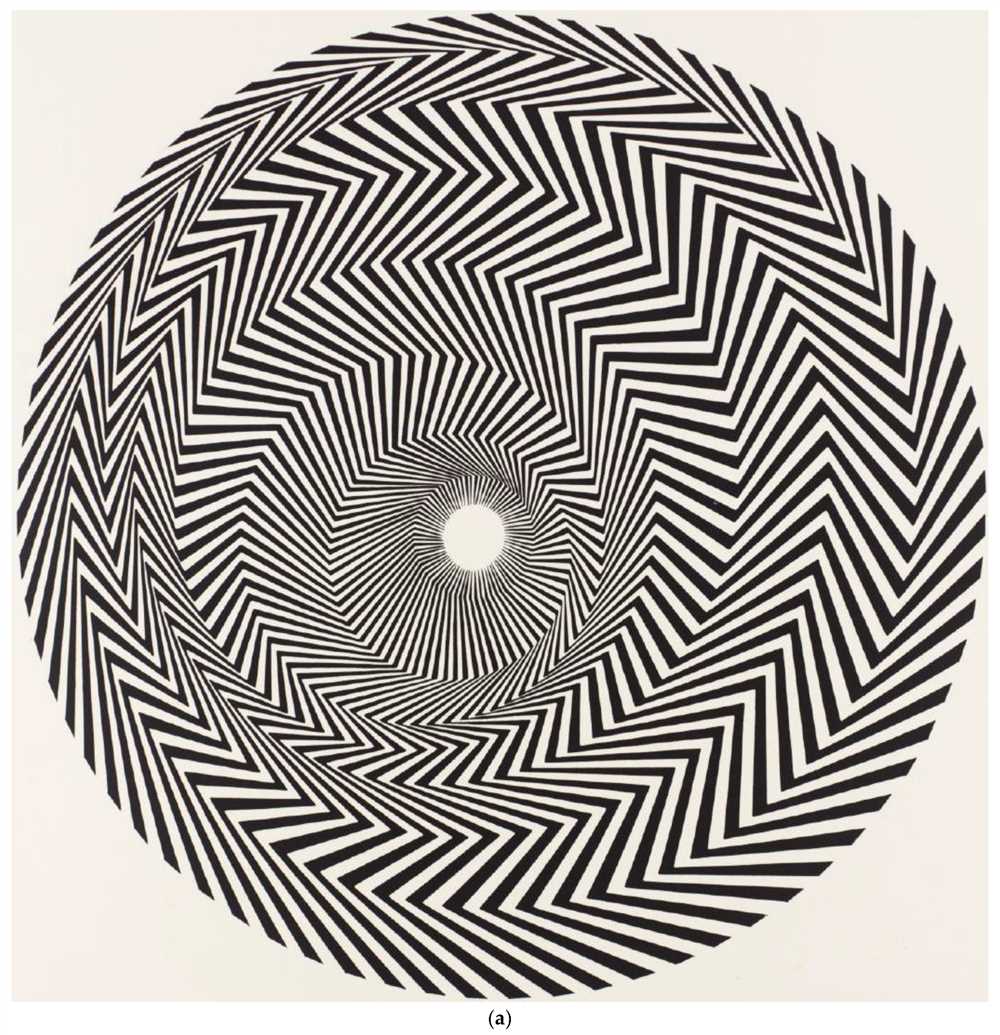

The world we perceive is not always a direct reflection of reality, as our mind often distorts the information transmitted by our senses. Optical illusions are a fascinating area of research that explores how our perception can be deceived by visual stimuli. These illusions have profound effects on our optical perception and can be used to gain a deeper understanding of the workings of the human mind.
Optical illusions are not simple tricks or visual gimmicks, but rather phenomena that reveal the complexities of our psychological processes. The science behind these illusions lies in the way our attention, interpretation, and perspective shape our perception. Illusions can simulate depth, manipulation of size, and even movement, tricking our brain into perceiving something that is not actually there.
One of the most striking aspects of optical illusions is how they challenge our cognitive awareness. These illusions exploit the way our brain processes information, creating a conflict between what we see and what we understand. As a result, our brain tries to reconcile these conflicting signals, often resulting in a distorted perception of reality.
Research into optical illusions has shown that our visual perception is not a passive process but an active construction of the world around us. Our brain is constantly interpreting visual input and making sense of it based on our past experiences and expectations. By understanding how our brain processes visual stimuli, we can gain insights into the complexity of human perception.
Beyond their scientific value, optical illusions also have practical implications. They are widely used in fields such as art, design, and advertising to evoke certain emotions or create visual effects. Additionally, understanding the psychological mechanisms behind optical illusions can help uncover how our brain processes information in general and may lead to new insights in fields such as neuroscience and psychology.
In conclusion, optical illusions are not just entertaining visuals – they provide a window into the inner workings of our mind. By exploring the psychological effects of these illusions, we can deepen our understanding of perception, cognition, and the remarkable capabilities of the human brain.
Cognitive Dissonance and Conflicting Perceptions
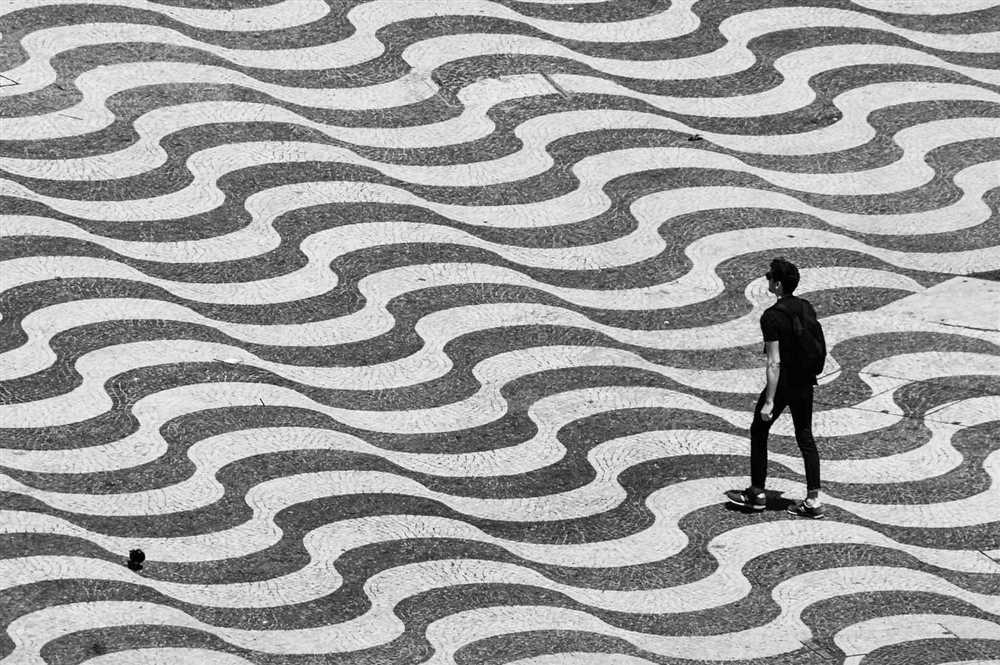

When it comes to optical illusions, our understanding of the mind goes beyond simple visual perception. The field of neuroscience has uncovered fascinating insights into how our attention and perception can be influenced by these perceptual distortions.
One phenomenon that researchers have identified is cognitive dissonance, which occurs when our brain receives conflicting information from our senses. This can happen when we encounter an optical illusion that challenges our usual interpretation of visual stimuli.
Optical illusions create a paradoxical situation for our mind. On one hand, we know that what we see is not aligned with reality, but on the other hand, our brain insists on interpreting these distortions as real. This conflict between what we perceive and what we know to be true creates cognitive dissonance.
Our brain is wired to interpret the world around us based on our previous experiences and understanding. When faced with an optical illusion, our brain tries to make sense of the conflicting information by creating a new interpretation that aligns with our existing knowledge. This process involves complex neural pathways and the activation of specific neurons that are responsible for perception.
The cognitive dissonance caused by optical illusions highlights the intricacies of our visual system and the limitations of our perception. It demonstrates that even though we may perceive something in a certain way, it does not necessarily correspond to reality.
Understanding the psychological effects of optical illusions goes beyond the visual experience. It raises questions about the nature of our awareness and the extent to which we can trust our own perception.
By studying optical illusions and the cognitive processes involved, researchers hope to gain a deeper understanding of how the brain processes visual information and how it can be deceived by these perceptual phenomena.
In conclusion, optical illusions are more than just visual tricks. They are windows into the complexities of our mind and the science of perception. By exploring cognitive dissonance and our conflicting perceptions, we can further unravel the mysteries of our visual system and broaden our understanding of the human brain.
What is an optical illusion?
An optical illusion is a visually perceived image that seems to differ from reality. It tricks our brain and makes us see things that are not actually there or distorts the true nature of the object.
How do optical illusions work?
Optical illusions work by taking advantage of the way our brain processes visual information. Our brain often makes assumptions and fills in missing pieces of the image. Illusions exploit these assumptions and use various visual tricks, such as perspective, contrast, and color, to deceive our perception.
What are the psychological effects of optical illusions?
Optical illusions can have a range of psychological effects on individuals. They can evoke feelings of confusion, surprise, and fascination. They can also challenge our perception of reality and make us question the reliability of our senses. Additionally, optical illusions have been used in psychological research to study cognitive processes and reveal insights into how our brain perceives and processes visual information.








+ There are no comments
Add yours