In today’s digital era, the way we view and value assets is undergoing a significant transformation. With the rise of blockchain technology, the concept of ownership and the market for collectibles has taken a whole new turn. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have emerged as a revolutionary innovation that allows for the tokenization of digital art, making it both verifiable and immutable.
Blockchain technology lies at the heart of this groundbreaking innovation, providing the necessary infrastructure for the creation and exchange of NFTs. It functions as a decentralized ledger, ensuring the security, transparency, and authentication of these unique tokens. Utilizing smart contracts, blockchain enables peer-to-peer transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries in the art market.
With NFT marketplaces gaining popularity, it is vital to comprehend the technology behind them. Tokenization is the process of converting a real-world or digital asset into a unique token on the blockchain. These tokens can represent anything from artworks and collectibles to virtual real estate and music albums. By digitizing these assets, their ownership becomes trackable and transferable without any ambiguity.
The blockchain technology used in NFT marketplaces also offers scalability and security. Transactions are stored in blocks, which are connected in chronological order, forming an unchangeable chain. This means that the information about an NFT’s ownership and transaction history remains intact, ensuring the authenticity and provenance of the digital asset. Additionally, the use of cryptography ensures the security of the blockchain, making it nearly impossible for anyone to tamper with the records.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology is the driving force behind the innovation and authentication of digital assets, such as NFTs, in peer-to-peer marketplaces. It is a decentralized ledger that enables the secure and transparent verification, ownership, and transfer of these unique collectibles.
At its core, blockchain is a distributed and immutable database that consists of a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions. These transactions can involve the exchange of cryptocurrencies, digital assets, or any form of value. The transactions are verified and added to the blockchain through consensus mechanisms, ensuring the integrity and security of the network.
The use of smart contracts on blockchain adds programmable functionality to transactions, enabling automatic execution and enforcement of predefined conditions. This facilitates the tokenization of assets, where physical or digital items are represented by tokens on the blockchain, creating a bridge between the physical and digital worlds.
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. Instead of storing data in a central authority or server, blockchain data is distributed across a network of computers, or nodes, which collectively maintain and validate the blockchain. This decentralization provides increased security and eliminates the need for intermediaries in transactions.
Blockchain also offers transparency and interoperability. As all transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be accessed, anyone can verify the authenticity and ownership of an asset. Additionally, blockchain allows for the seamless integration of various systems and platforms, enabling the exchange and transfer of assets across different marketplaces and ecosystems.
The blockchain technology has revolutionized the way digital assets, including NFTs, are created, owned, and traded. Its scalability, security, and efficiency make it an ideal solution for the rapidly growing NFT marketplaces, where artists and collectors can interact and transact with confidence.
Definition and key features
In the world of digital art and collectibles, blockchain technology has been breaking down barriers and revolutionizing the way we buy, sell, and trade assets. One of the most exciting developments in this space is the rise of NFT marketplaces.
NFT stands for Non-Fungible Token, which means it is a unique token that represents ownership of a specific digital asset. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are interchangeable and can be exchanged on a one-to-one basis, NFTs are one-of-a-kind and cannot be replaced or substituted.
NFT marketplaces serve as platforms where artists, creators, and collectors can interact in a peer-to-peer manner, buying and selling digital art, virtual assets, and collectibles. These marketplaces leverage blockchain technology to provide various key features:
- Immutability: NFTs are stored on a blockchain, making them immutable and resistant to tampering. This ensures the authenticity and provenance of the digital assets.
- Decentralization: NFT marketplaces are built on decentralized blockchain networks, which means there is no central authority controlling the transactions or ownership of the assets. This enhances transparency and reduces the risk of censorship.
- Smart contracts: NFT marketplaces utilize smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with predetermined rules and conditions. These contracts facilitate automated transactions and enforce the terms of the sale, ensuring a secure and trustworthy environment.
- Tokenization: NFTs represent the tokenization of assets, meaning they can represent ownership or partial ownership of any digital item, including art, music, videos, virtual real estate, and more. This allows for fractional ownership and easy transferability of these assets.
- Verification and authentication: NFT marketplaces provide a transparent and verifiable record of ownership and provenance. This can help prevent fraud and ensure that artists receive proper attribution and royalties for their work.
- Interoperability: With the use of blockchain technology, NFTs can be easily interoperable across different platforms and marketplaces. This allows for greater liquidity and a larger pool of potential buyers and sellers.
- Scalability: Blockchain technology offers scalability, allowing NFT marketplaces to handle a large volume of transactions without compromising performance or security.
- Security: The decentralized nature of blockchain technology provides a high level of security for NFT marketplaces. Transactions are secured through cryptographic algorithms, and the distributed ledger ensures that no single point of failure can compromise the security of the platform.
In conclusion, NFT marketplaces leverage blockchain technology to provide a secure, transparent, and innovative platform for buying, selling, and trading digital assets. These marketplaces offer a new way to appreciate and value digital art and collectibles while democratizing ownership and empowering creators.
How does it work?
The technology behind NFT marketplaces is built on the smart and decentralized concept of blockchain. Blockchain is a digital ledger that records all transactions in a transparent and secure manner. It consists of a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions.
NFTs are created using smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into the code. These contracts ensure the security and authenticity of the NFTs. Smart contracts enable the tokenization of digital assets, such as art and collectibles, representing ownership and providing proof of authenticity.
Blockchain technology allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries. It provides security through cryptographic algorithms and verification processes. NFTs can be bought, sold, and traded on the marketplace using cryptocurrency as a means of exchange.
The transparency and interoperability of blockchain technology make it possible for NFT marketplaces to authenticate and verify the ownership of digital assets. Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain, creating a transparent and immutable record of ownership.
Moreover, blockchain technology brings innovation to the concept of ownership, allowing for fractional ownership and the creation of new revenue streams for creators. It also opens up opportunities for global participation, as anyone with an internet connection can access and participate in NFT marketplaces.
Scalability is another important aspect of NFT marketplaces. With blockchain technology, these marketplaces can handle a large number of transactions simultaneously, ensuring a smooth and efficient trading experience.
In conclusion, the technology behind NFT marketplaces is based on the smart and decentralized nature of blockchain. It offers security, transparency, and interoperability, allowing for the tokenization and trading of digital assets. Through blockchain technology, NFT marketplaces have revolutionized the concept of ownership and created new opportunities for artists and collectors.
Role of Blockchain in NFT Marketplaces
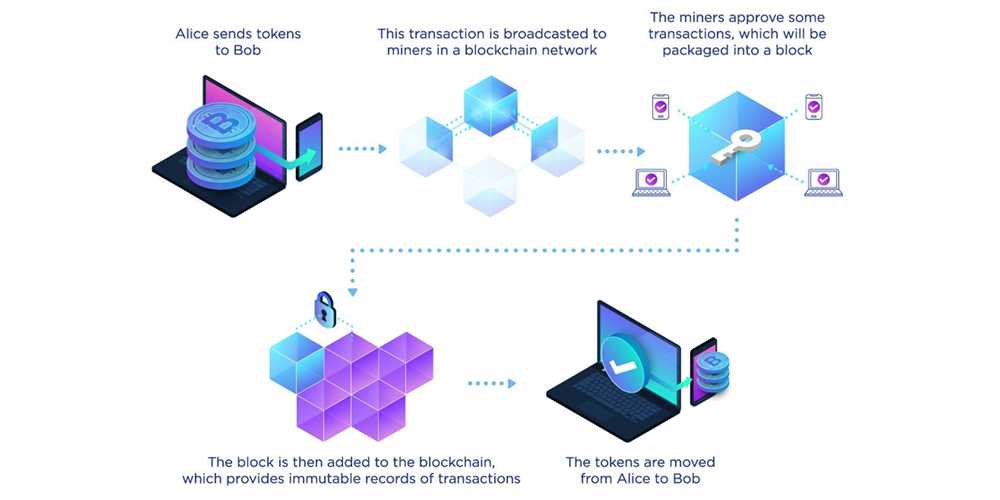
Blockchain plays a crucial role in the functioning of NFT marketplaces, revolutionizing the way art and digital assets are bought, sold, and owned. By breaking down the technology behind NFT marketplaces, we can understand the integral role that blockchain technology plays in this innovative space.
One of the core functionalities of blockchain in NFT marketplaces is verification and authentication. Due to the transparent and immutable nature of the blockchain ledger, buyers can be confident in the authenticity and ownership of their digital collectibles. Blockchain technology ensures that each token is unique, providing a level of scarcity and value to digital assets.
Furthermore, blockchain enables decentralized and peer-to-peer transactions within NFT marketplaces. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, blockchain technology allows artists and creators to directly connect with buyers, facilitating a more efficient and cost-effective marketplace. Additionally, smart contracts on the blockchain enable automated transactions, eliminating the need for manual processes and streamlining the buying and selling experience.
Scalability and interoperability are also key benefits of blockchain in NFT marketplaces. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and improve, it provides a scalable and efficient infrastructure for handling the growing demand for digital art and collectibles. Moreover, blockchain’s interoperability allows for seamless integration with other platforms and ecosystems, expanding the reach and potential of NFT marketplaces.
Another important aspect of blockchain in NFT marketplaces is the role it plays in security. With the use of cryptographic algorithms and protocols, blockchain technology ensures the secure transfer and storage of digital assets. This is particularly important in the case of high-value art and collectibles, where the security of ownership and provenance is paramount.
In conclusion, blockchain technology underpins the functioning of NFT marketplaces, providing transparency, security, and innovation to the world of digital art and collectibles. By leveraging tokenization and smart contracts, NFT marketplaces are able to revolutionize the way we buy, sell, and own digital assets, opening up new opportunities for artists, collectors, and enthusiasts.
Understanding NFTs

NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, are an innovative technology built on the foundation of blockchain. They have gained significant attention in recent years, particularly in the art world, for their unique ability to represent ownership and authenticity in the digital realm.
Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, which are fungible and can be exchanged on a one-to-one basis, NFTs are unique and cannot be exchanged on a like-for-like basis. Each NFT is associated with a specific digital asset, whether it be a piece of art, a collectible, or any other form of digital content.
One of the key features of NFTs is their ability to utilize smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These smart contracts enable the automation of various tasks, such as the transfer of ownership or the payment of royalties to the original creator when an NFT is sold in a marketplace.
Furthermore, NFTs offer peer-to-peer transactions, allowing buyers and sellers to interact directly without the need for intermediaries. This decentralized nature ensures transparency and security, as all transactions are recorded on a public ledger, known as the blockchain.
Tokenization is another fundamental aspect of NFTs. Assets, whether they are digital or physical, can be tokenized and represented as NFTs. This tokenization process converts the asset into a digital token, which can then be bought, sold, and traded on various NFT marketplaces.
One of the key advantages of NFTs is their ability to provide authentication and provenance for digital assets. By leveraging blockchain technology, NFTs create an immutable record of ownership, tracing the entire history of an asset from its creation to its current owner.
Additionally, NFTs have opened up new opportunities for artists and creators to monetize their work in a decentralized and accessible manner. With the rise of NFT marketplaces, artists can now directly sell their digital creations to a global audience, bypassing traditional gatekeepers in the art world.
However, it is important to note that NFTs are not without limitations. One of the main challenges is scalability, as the current blockchain infrastructure can struggle to handle high volumes of NFT transactions. This has led to issues such as high transaction fees and slow transaction times.
Despite these challenges, NFTs have undoubtedly revolutionized the way we perceive and engage with digital assets. Their combination of ownership, contracts, art, and innovation has paved the way for new possibilities in the digital realm and has sparked a wave of creativity and exploration within the blockchain ecosystem.
Definition and characteristics

Blockchain technology is the backbone of the NFT marketplaces, providing a secure and transparent framework for digital asset ownership. It is a decentralized ledger that records transactions in a series of blocks, where each block is linked to the previous one, creating an immutable chain of information.
One of the key characteristics of blockchain technology is its peer-to-peer nature, meaning that transactions can be conducted directly between parties without the need for intermediaries. This eliminates the need for centralized authorities and opens up new possibilities for innovation and collaboration.
Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into the code, play a crucial role in NFT marketplaces. These contracts enable the automatic verification, authentication, and transfer of ownership of digital assets, such as art or collectibles, in a secure and transparent manner.
Tokenization is another important concept in blockchain technology. By tokenizing assets, such as art or real estate, they can be represented as unique tokens on the blockchain, providing a way to prove ownership and enabling easy transferability. This facilitates the creation of NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, which are unique digital assets that cannot be replicated or replaced.
Security is a fundamental aspect of blockchain technology. The use of cryptographic techniques ensures the integrity and confidentiality of the data stored on the blockchain, protecting it from tampering or unauthorized access. This makes blockchain technology an ideal solution for securing the ownership and provenance of valuable digital assets.
Transparency is another key characteristic of blockchain technology. Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is visible to all participants, providing a high level of transparency and accountability. This transparency helps to build trust among participants and ensures the integrity of the marketplace.
Furthermore, blockchain technology enables interoperability, allowing different NFT marketplaces to communicate and interact with each other. This opens up new possibilities for collaboration and the exchange of assets between different platforms, increasing the liquidity and value of the NFT market.
Scalability is an ongoing challenge for blockchain technology, as the number of transactions and participants in NFT marketplaces continues to grow. However, technological advancements and improvements are being made to address this issue and ensure the scalability of blockchain networks.
In summary, blockchain technology is the underlying technology powering NFT marketplaces, providing a secure, transparent, and decentralized framework for the creation, authentication, and transfer of digital assets. Through its innovation in authentication, verification, and ownership, blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we understand and interact with digital art and collectibles.
Question-answer:
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It provides an open and transparent way to verify and secure transactions, making it difficult for any individual or entity to manipulate or tamper with the data.
How does blockchain technology work?
Blockchain technology works by creating a network of computers, known as nodes, that collectively maintain a shared ledger of transactions. Each transaction is bundled into a block, which is then added to the chain of previous blocks in a chronological order. This chain of blocks is publicly accessible and provides a transparent record of all transactions that have occurred.








+ There are no comments
Add yours