
NFT (Non-Fungible Token) blockchains have taken the digital world by storm, revolutionizing the way we think about ownership and authenticity in the digital space. These unique tokens represent ownership or proof of authenticity for a specific digital asset, such as art, music, videos, or virtual real estate. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are fungible and can be exchanged on a one-to-one basis, NFTs are indivisible and unique, making them perfect for representing rare or limited-edition digital items.
So, what sets NFT blockchains apart from other blockchain platforms? One of the key features of NFT blockchains is their ability to store metadata alongside the token itself. This metadata can include details about the digital asset, such as its creator, the date it was created, its history, and even additional information like links to its original source or related content. This makes NFT blockchains a powerful tool for provenance and authentication, allowing users to verify the origins and ownership of a digital asset with ease.
Another important feature of NFT blockchains is their support for smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that automatically enforce the terms and conditions of a transaction. In the context of NFTs, smart contracts can be used to automate the transfer of ownership or the distribution of royalties to content creators, ensuring that the original creators receive their fair share of the profits whenever their NFT is bought, sold, or used in any way.
In addition to these features, NFT blockchains also provide a decentralized and transparent environment for creators and collectors alike. These blockchains are typically public, meaning that anyone can access and verify the information stored on them. This not only promotes transparency and trust but also allows for the development of secondary markets where users can buy, sell, or trade NFTs without relying on a centralized authority.
In conclusion, NFT blockchains offer a unique set of features and functionalities that set them apart from other blockchain platforms. From storing metadata alongside tokens to supporting smart contracts and fostering transparency, NFT blockchains have the potential to revolutionize how we create, sell, and collect digital assets. Whether you are an artist, a collector, or simply curious about the digital world, exploring the world of NFT blockchains is an exciting and rewarding journey that promises to unlock new possibilities in the digital space.
What are NFTs?

NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, have gained significant attention and popularity in recent years. Essentially, NFTs are unique digital assets that are created, bought, and sold on blockchain networks. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are fungible and can be exchanged with one another on a one-to-one basis, NFTs cannot be exchanged for another token of equal value.
NFTs represent ownership or proof of authenticity of a particular digital item, such as artwork, music, videos, virtual real estate, and even virtual pets. Each NFT is assigned a unique identifier, which makes it distinct from all other tokens on the blockchain.
How Do NFTs Work?

NFTs are built on blockchain technology, which provides a decentralized and transparent ledger for recording ownership and transaction history. Most NFTs are based on Ethereum’s blockchain, utilizing its ERC-721 token standard. However, other blockchain networks such as Binance Smart Chain and Flow have also developed their own NFT standards.
When an NFT is created, it is assigned a smart contract that defines its properties and rules. This contract includes details such as the creator’s royalties, the total supply of the NFT, and any additional conditions for its use or resale.
The Value and Market for NFTs

The value of an NFT is determined by various factors, including its scarcity, uniqueness, demand, and the reputation of its creator. Some NFTs have sold for astounding amounts, reaching millions of dollars in auctions and marketplaces.
The NFT market has seen rapid growth, attracting artists, musicians, creators, collectors, and investors. NFTs provide new opportunities for artists to monetize their digital creations and establish direct connections with their audience, cutting out intermediaries.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Unique digital ownership | Environmental impact of blockchain networks |
| Increased market access for creators | Lack of regulations and potential scams |
| Traceability and authenticity | Volatility and speculation |
Despite the controversies and challenges, NFTs continue to drive innovation and disrupt traditional industries. As more blockchain networks develop their own NFT standards, it is likely that NFTs will become an integral part of the digital economy.
Key Features of NFT Blockchains
NFT blockchains offer a range of unique features that make them suitable for hosting and managing non-fungible tokens. These key features include:
1. Immutable Ledger: NFT blockchains utilize distributed ledger technology, which ensures that all transactions and ownership records are securely stored and cannot be altered or tampered with.
2. Interoperability: NFT blockchains can interact with other blockchain networks and smart contracts, allowing for seamless integration and the ability to transfer tokens between different platforms.
3. Token Standardization: NFT blockchains often implement token standards, such as the ERC-721 or ERC-1155 standards for Ethereum, ensuring that tokens can be easily recognized, traded, and understood by different applications and wallets.
4. Fractional Ownership: NFT blockchains enable fractional ownership, meaning that a single NFT can be divided into smaller shares, allowing multiple individuals to collectively own a piece of the token.
5. Provably Scarce: NFT blockchains provide a provably scarce environment, with each token containing unique metadata and attributes that cannot be replicated or counterfeited.
6. Decentralized Marketplace: NFT blockchains often have built-in decentralized marketplaces, where users can buy, sell, and trade their tokens directly, without the need for intermediaries or centralized platforms.
7. Smart Contract Functionality: NFT blockchains leverage smart contracts, which enable the execution of programmable logic and automation, allowing for the implementation of complex functionalities such as royalties and automated distribution of revenue.
8. Ecosystem and Community: NFT blockchains foster vibrant communities and ecosystems, with developers, artists, collectors, and enthusiasts coming together to create, showcase, and support NFT-based projects and applications.
These key features contribute to the widespread adoption and success of NFT blockchains, enabling the exploration and development of novel use cases and unlocking new opportunities in digital ownership and creative expression.
Exploring the Functionality of NFT Blockchains

Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have gained significant popularity in recent years. NFTs are unique digital assets that can be bought, sold, and traded on blockchain platforms. These tokens have brought a new level of functionality to blockchain technology, allowing for the ownership and transfer of digital assets in a secure and transparent manner.
Interoperability
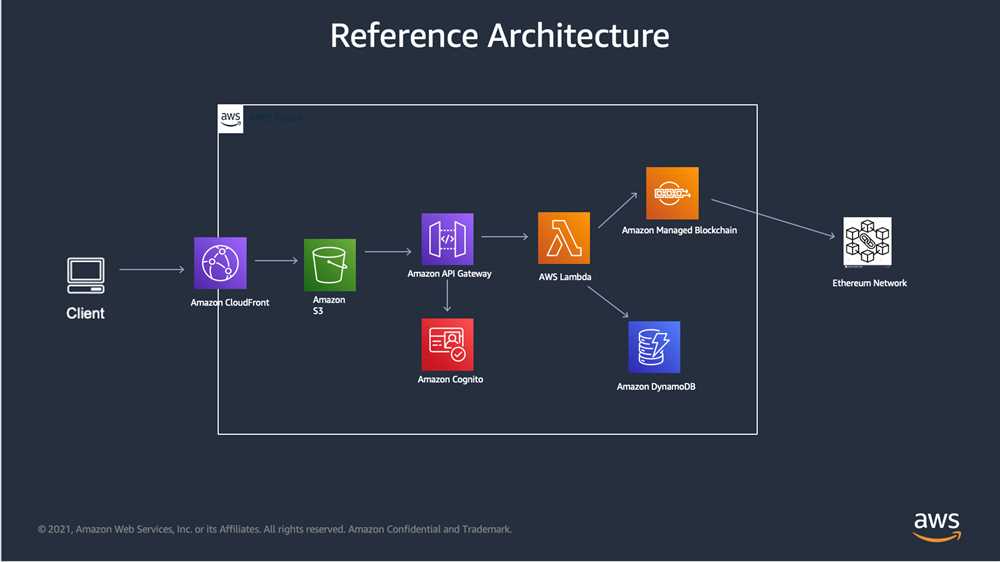
One key functionality of NFT blockchains is interoperability. NFTs can be created and traded across multiple blockchain platforms, allowing for seamless integration and interaction between different ecosystems. This means that an NFT created on one blockchain can be easily transferred and utilized on another blockchain, opening up a world of possibilities for creators and collectors.
Smart Contracts

NFT blockchains are powered by smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into the code. Smart contracts enable the automatic execution of transactions and the enforcement of ownership rights for NFTs. This functionality ensures that the ownership and transfer of NFTs are carried out securely and without the need for intermediaries.
NFT blockchains also provide additional functionality through the use of smart contracts. These contracts can include various conditions and rules for the use and licensing of NFTs, allowing creators to retain certain rights or set specific terms for the sale and distribution of their digital assets.
In conclusion, NFT blockchains offer a range of functionalities that have revolutionized the world of digital assets. From interoperability to smart contracts, these platforms provide a secure and efficient way for creators and collectors to buy, sell, and trade unique digital assets. As the popularity of NFTs continues to grow, it is likely that we will see even more innovative functionalities emerge in this exciting and rapidly evolving space.
What are NFTs and how do they work?
NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, are unique digital assets that are stored on a blockchain. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are fungible and can be exchanged on a one-to-one basis, NFTs cannot be exchanged on a like-for-like basis as each one is unique. NFTs work by using blockchain technology to provide a record of ownership and authenticity for digital assets, such as artwork, videos, music, or virtual real estate.
Which blockchain platforms are commonly used for NFTs?
There are several blockchain platforms that are commonly used for NFTs, with Ethereum being the most popular one. Ethereum’s ERC-721 and ERC-1155 standards have become the de facto standards for creating and trading NFTs. Other blockchain platforms such as Binance Smart Chain, Flow, Tezos, and Solana have also gained popularity in the NFT space.







+ There are no comments
Add yours